

Simple random sampling is a statistical method in which everyone in a population has an equal chance of being selected into a sample. The sample represents a smaller and more manageable portion of the people that can be studied and analyzed. It’s a fundamental technique to gather data and make inferences about a population.
Simple random sampling is considered a fair and unbiased sample selection method. This type of sampling is the most straightforward sample selection bias method.
Content Index hideSimple random sampling is a technique where every item in the population has an even chance and likelihood of being selected. Here, the selection of items entirely depends on luck or probability. Therefore, this sampling technique is also a method of chance.
Simple random sampling is a fundamental method and can easily be a component of a more complex method. The main attribute of this sampling method is that every sample has the same probability of being chosen.
The sample size in a simple random sampling method should ideally be more than a few hundred so that it can be applied appropriately. This method is theoretically simple to understand but difficult to implement practically. Working with a large sample size isn’t an easy task, and it can sometimes be challenging to find a realistic sampling bias frame.
Researchers follow these methods to select a simple random sample:
Two approaches aim to minimize any biases in the process of this method:
Using the lottery method is one of the oldest ways and is a mechanical example of a random sample. Researchers draw numbers from the box randomly to choose samples. In this method, the researcher gives each member of the population a number.
Using random numbers is an alternative method that also involves numbering the population. A numbered table similar to the one below can help with this sampling technique.
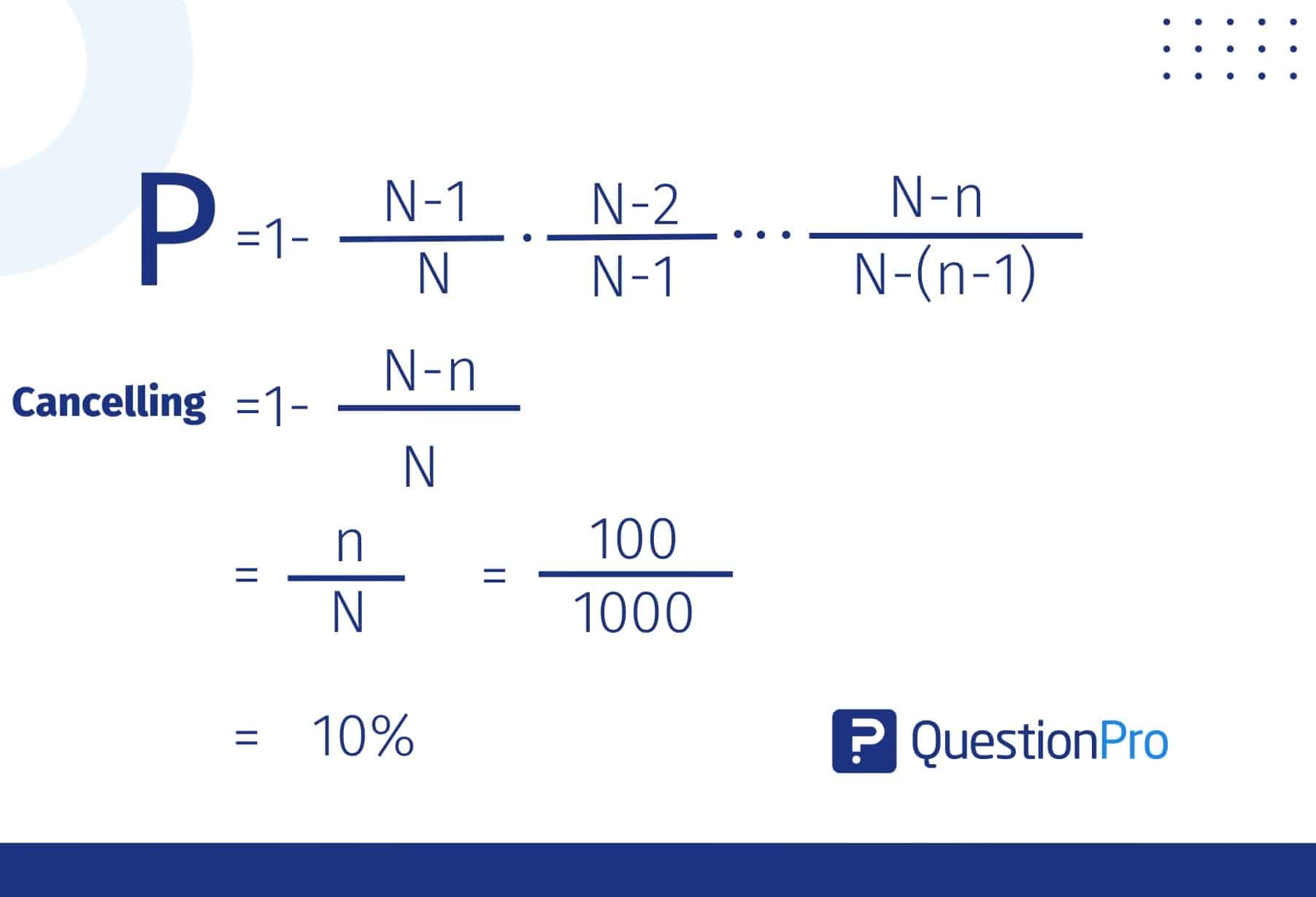
Consider that a hospital has 1000 staff members and must allocate a night shift to 100 members. All their names will be put in a bucket to be randomly selected. Since each person has an equal chance of being selected. Since we know the population size (N) and sample size (n), the calculation can be as follows:
Simple random sampling is a crucial method in statistical analysis for drawing unbiased conclusions about a population. Below are the steps to perform simple random sampling to select a sample of 100 employees out of a total of 500 in an organization.
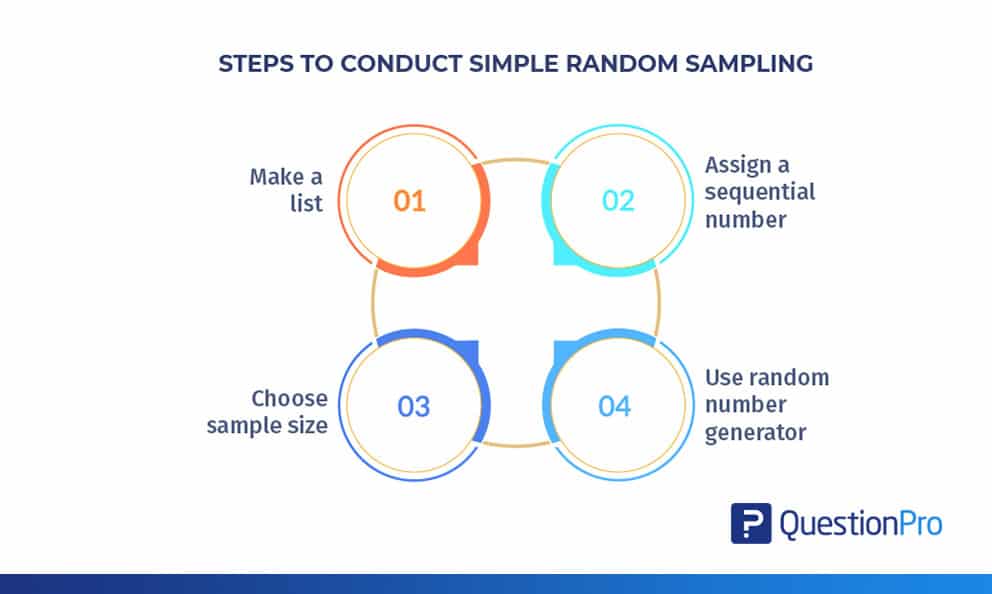
To start simple random sampling, first, make a complete list of all 500 employees in the organization. It’s important that the list includes the names of every employee to guarantee that each person is considered.
A precise and thorough list is crucial to ensure the sampling accurately reflects the entire population.
After creating the list of employees, the next thing to do is give each employee a number in order. This is your sampling frame (the list from which you draw your sample). This numbering helps organize the list, making identifying each person in the group easier.
Every employee should have their own number, starting from 1 and going up to n, which is the total number of employees in the organization.
Selecting the right sample size is important in simple random sampling. In this situation, we’ve chosen a sample of 100 employees from a total population of 500. It’s essential to pick a sample size that’s large enough for dependable results but still practical for analysis.
To choose a sample from the group, use a random number generator. First, find the total number of people (Step 2) and decide how many we want in our sample (Step 3).
Then, use a random number table or generator to create 100 different random numbers between 1 and 500. These numbers match the order given to each employee, which helps you pick who will be in the sample.
This method ensures that each employee has an equal opportunity for selection, maintaining fairness and impartiality in sample selection.
It is important to note that Simple Random Sampling is just one of many sampling methods available, and it may not always be the best option for your specific research needs.
When thinking about how to sample, people often look at different methods like simple random sampling, stratified sampling, systematic sampling, and cluster sampling. Each method has its pros and cons, so it’s crucial to choose the right one depending on what you’re studying and the features of the group you’re looking at.
The simple random sampling techniques and stratified random sampling have different ways of choosing samples from a population.
While simple random samples treat each individual in the population as a potential sample unit, cluster sampling involves grouping individuals into clusters or natural units before selecting samples.
Systematic sampling involves selecting samples at regular intervals after starting randomly.
Today’s market research projects are much larger and involve an indefinite number of items. It is practically impossible to study every member of the population’s thought process and derive interference from the study.
If, as a researcher, you want to save your time and money, simple random sampling is one of the best probability sampling methods that you can use. Getting data from a sample is more advisable and practical.
Using a census or a sample depends on several factors, such as the type of census, the degree of homogeneity/heterogeneity, costs, time, feasibility of study, the degree of accuracy needed, etc.
Simple random sampling has several advantages, including:
Overall, this is a valuable and versatile method for gathering data and making inferences about populations.
Simple random sampling has some drawbacks that can affect the relevance of the collected data:
Researchers use simple random sampling in statistical analysis methods valuable for various applications. Selecting a sample of individuals from a population in a random and unbiased manner provides a representative sample and a cost-effective way of gathering data and making inferences about populations.
With QuestionPro, researchers and data analysts can easily and efficiently implement simple random sampling in their research and studies. We are here to help to ensure that the results are accurate.
If you’re a market researcher trying to learn more about your target audience or a social scientist aiming to study a population, Simple Random Sampling with QuestionPro is a dependable and efficient method to explore.